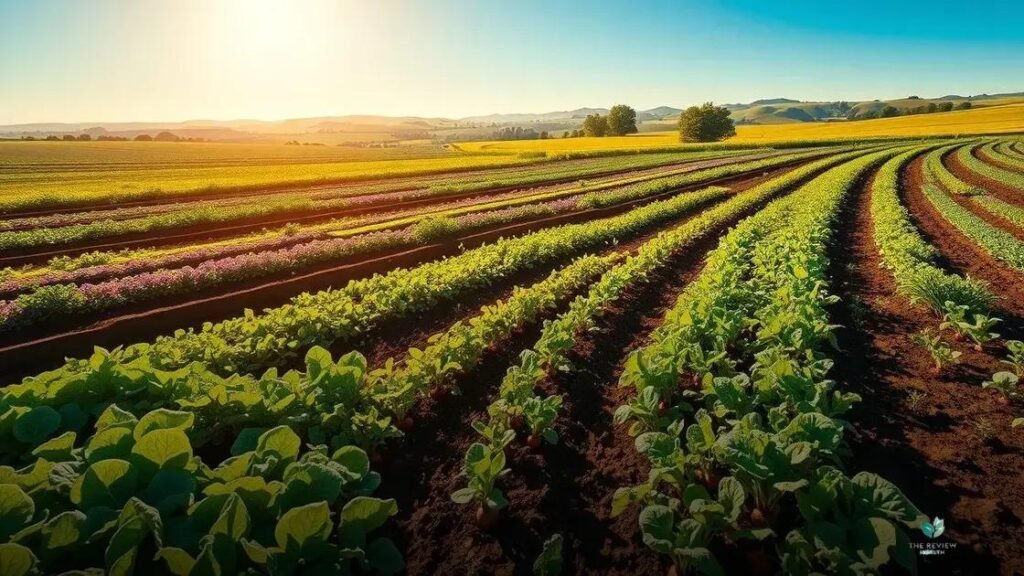
Regenerative agriculture is a holistic land management approach that improves soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem services while enhancing farm resilience and mitigating climate change through carbon sequestration.
Regenerative agriculture is more than just a farming method; it’s a way to reconnect with our food and the earth. Have you ever considered how what you eat affects the planet? This approach prioritizes soil health, biodiversity, and sustainable nutrition.
understanding regenerative agriculture
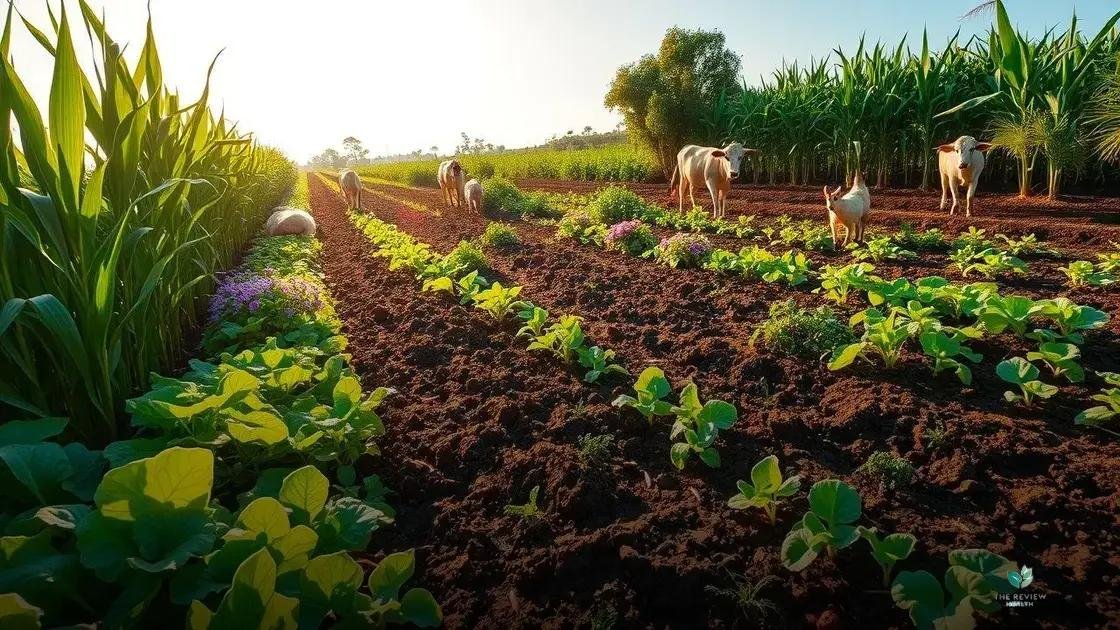

Understanding regenerative agriculture goes beyond simply growing food; it’s about restoring and revitalizing the entire ecosystem. It’s a holistic approach that recognizes the interconnectedness of everything from the smallest soil microbe to the largest grazing animal.
What is Regenerative Agriculture?
Unlike conventional farming, which often depletes soil health and biodiversity, regenerative agriculture focuses on building these crucial elements. Think of it as nurturing the land, rather than just extracting from it. This approach prioritizes practices that improve soil health, increase biodiversity, enhance water cycles, support carbon sequestration, and strengthen the resilience of farms and communities.
Key Principles of Regenerative Agriculture
- Minimizing Soil Disturbance: Practices like no-till farming help protect the soil structure and the beneficial organisms living within it.
- Maximizing Crop Diversity: Planting a variety of crops mimics natural ecosystems and helps build soil fertility.
- Integrating Livestock: Animals play a crucial role in nutrient cycling and soil health when managed responsibly.
- Continuous Living Cover: Keeping the soil covered with plants or mulch helps prevent erosion and improves water infiltration.
Why is Regenerative Agriculture Important?
Regenerative agriculture offers a solution to many of the challenges facing our current food system. It helps combat climate change by sequestering carbon in the soil. It improves water quality and availability. It enhances the nutritional value of our food. And it creates more resilient and profitable farms for future generations. By shifting our focus from extraction to regeneration, we can create a healthier and more sustainable food future.
key practices that make a difference
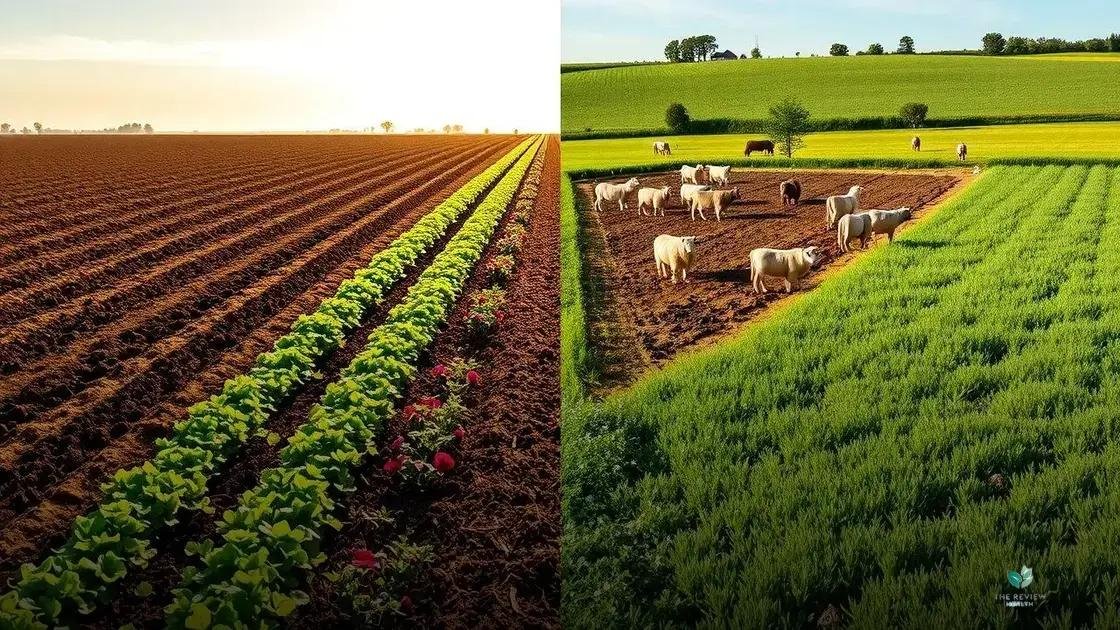

Key practices distinguish regenerative agriculture from conventional methods, driving its positive impact on the environment and food production. These practices work together to create a synergistic effect, enhancing soil health, biodiversity, and farm resilience.
No-Till Farming
Disturbing the soil through tillage can disrupt its structure, release stored carbon, and harm beneficial microbes. No-till farming minimizes soil disturbance, allowing the soil ecosystem to thrive. This practice improves water infiltration, reduces erosion, and enhances carbon sequestration.
Cover Cropping
Cover crops, planted between cash crops or during fallow periods, play a vital role in soil health. They prevent erosion, suppress weeds, improve soil fertility, and enhance biodiversity by providing habitat for beneficial insects and pollinators.
Crop Rotation
Rotating different crops helps maintain soil fertility and reduces pest and disease pressure. Different crops have different nutrient needs, and rotating them helps prevent nutrient depletion. It also disrupts pest and disease cycles, reducing the need for chemical interventions.
Composting and Manure Management
Composting and responsible manure management return valuable nutrients to the soil, improving its structure and fertility. These practices reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers, promoting a more natural and sustainable approach to soil health.
Integrating Livestock
Managed grazing, where livestock are strategically moved across pastures, can mimic natural grazing patterns. This practice helps improve soil health, stimulate plant growth, and enhance biodiversity. The animals’ manure also acts as a natural fertilizer.
By implementing these key practices, farmers can transition towards a more sustainable and regenerative system that benefits both the environment and their bottom line.
how regenerative agriculture combats climate change
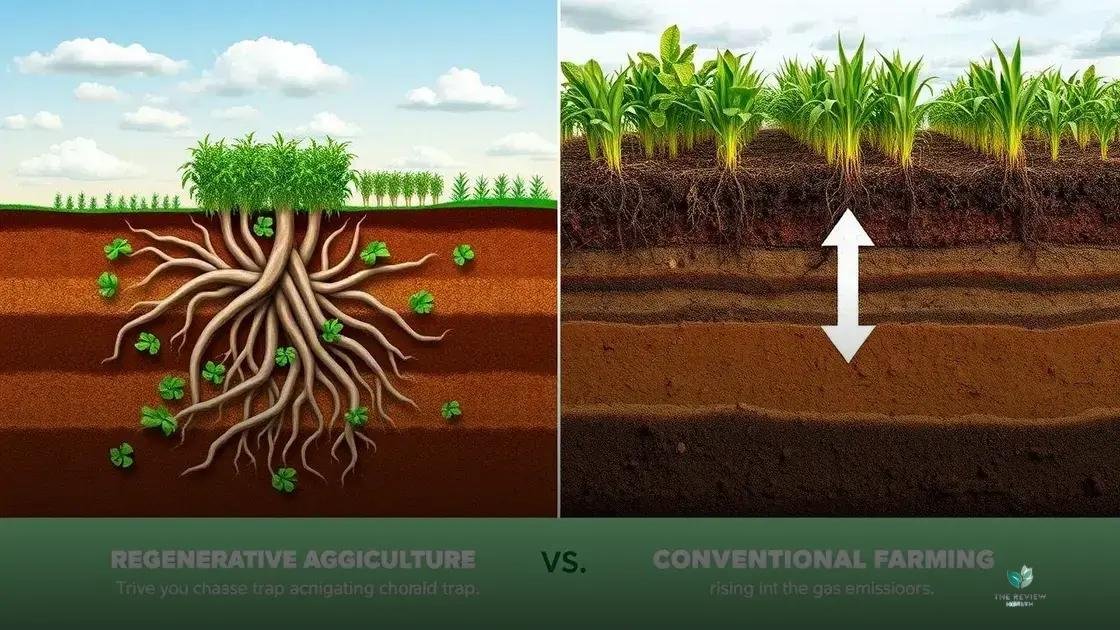
Regenerative agriculture offers a powerful tool in the fight against climate change. By focusing on soil health, this approach helps sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, turning agricultural land into a carbon sink rather than a source.
Carbon Sequestration
Healthy soil acts like a sponge, absorbing and storing carbon dioxide from the air. Regenerative practices, such as no-till farming and cover cropping, enhance this process. By minimizing soil disturbance and maximizing plant cover, these methods increase the amount of carbon stored in the soil, effectively removing it from the atmosphere.
Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Conventional agriculture often relies on synthetic fertilizers and intensive tillage, which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. Regenerative agriculture reduces these emissions by minimizing the need for synthetic inputs and promoting natural nutrient cycling. Healthy soil also requires less irrigation, further reducing the carbon footprint of food production.
Enhanced Soil Health and Resilience
Healthy soil is more resilient to the impacts of climate change, such as drought and extreme weather events. Improved water infiltration and retention help mitigate drought conditions. Strong soil structure reduces erosion and runoff during heavy rainfall. These benefits ensure that farms can continue to produce food even in a changing climate.
A Holistic Approach
Regenerative agriculture takes a holistic approach to climate change mitigation and adaptation. It addresses the root causes of the problem by restoring the health of our ecosystems. This approach not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also creates more resilient farms and communities that can withstand the challenges of a changing climate.
The Future of Food and Farming
Regenerative agriculture represents a shift in our thinking about food production—moving from extraction to regeneration. By embracing these practices, we can create a more sustainable and resilient food system that benefits both people and the planet. From improving soil health and sequestering carbon to enhancing biodiversity and creating healthier food, regenerative agriculture offers a path towards a brighter future. It’s a journey that requires collaboration, innovation, and a commitment to working in harmony with nature. And it’s a journey worth taking.
FAQ – Regenerative Agriculture
What is regenerative agriculture?
Regenerative agriculture is a farming approach that focuses on improving soil health, increasing biodiversity, and enhancing ecosystem services. It goes beyond sustainable agriculture by aiming to actively restore and revitalize agricultural land.
How does regenerative agriculture help fight climate change?
Regenerative practices, like no-till farming and cover cropping, help sequester carbon in the soil, removing it from the atmosphere. It also reduces greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture.
What are the key practices of regenerative agriculture?
Key practices include no-till farming, cover cropping, crop rotation, composting, manure management, and integrating livestock.
Is regenerative agriculture more expensive than conventional farming?
While there can be upfront costs associated with transitioning to regenerative practices, long-term benefits such as reduced inputs (fertilizers, pesticides) and increased yields can make it economically viable.
How can I support regenerative agriculture?
Support regenerative agriculture by buying products from farms that use these practices. Look for certifications or labels that indicate regenerative production. You can also advocate for policies that support regenerative agriculture.
What are the benefits of regenerative agriculture for consumers?
Regenerative agriculture can lead to more nutrient-dense food, improved water quality, and a more resilient food supply. It also contributes to a healthier environment.

Sarah Thompson is a passionate advocate for healthy living and mindful lifestyle choices. With a background in nutrition science and years of experience as a wellness coach, Sarah dedicates her time to exploring the latest trends, research, and products that promote physical, mental, and emotional well-being.
As the lead writer for The Review Health , Sarah combines her expertise with a genuine love for helping others make informed decisions about their health. Her articles are designed to inspire and educate, offering practical tips, honest reviews, and science-backed insights to support readers on their journey to a healthier, happier life.
When she’s not writing or researching, Sarah enjoys yoga, experimenting with plant-based recipes, and spending time outdoors with her family.



